There is currently no treatment to “reverse” Type 1 Diabetes. Type 2 Diabetes can sometimes be “reversed” by weight loss and exercise.
There is no treatment to prevent Type 1 diabetes. Type 2 Diabetes can be prevented by weight loss and exercise (see info on Pre-diabetes)
A1C is a blood test done by the lab, which reflects overall control of Diabetes, dating back 3 months. The A1C target according to ADA is <7% . This level is associated with a low level of complications of Diabetes. The target A1C should be individualized depending on a number of relevant factors such as age and duration of Diabetes.
The A1c should be done no more often than every 3 months. The A1C test measures part of the red blood cell hemoglobin. Red blood cells live 3-4 months, and one of the hemoglobin fractions in the red blood cell is the A1C. This fraction irreversibly attaches sugar which crosses the red cell membrane. The A1C, then, offers a 3-month barometer of overall Diabetes control
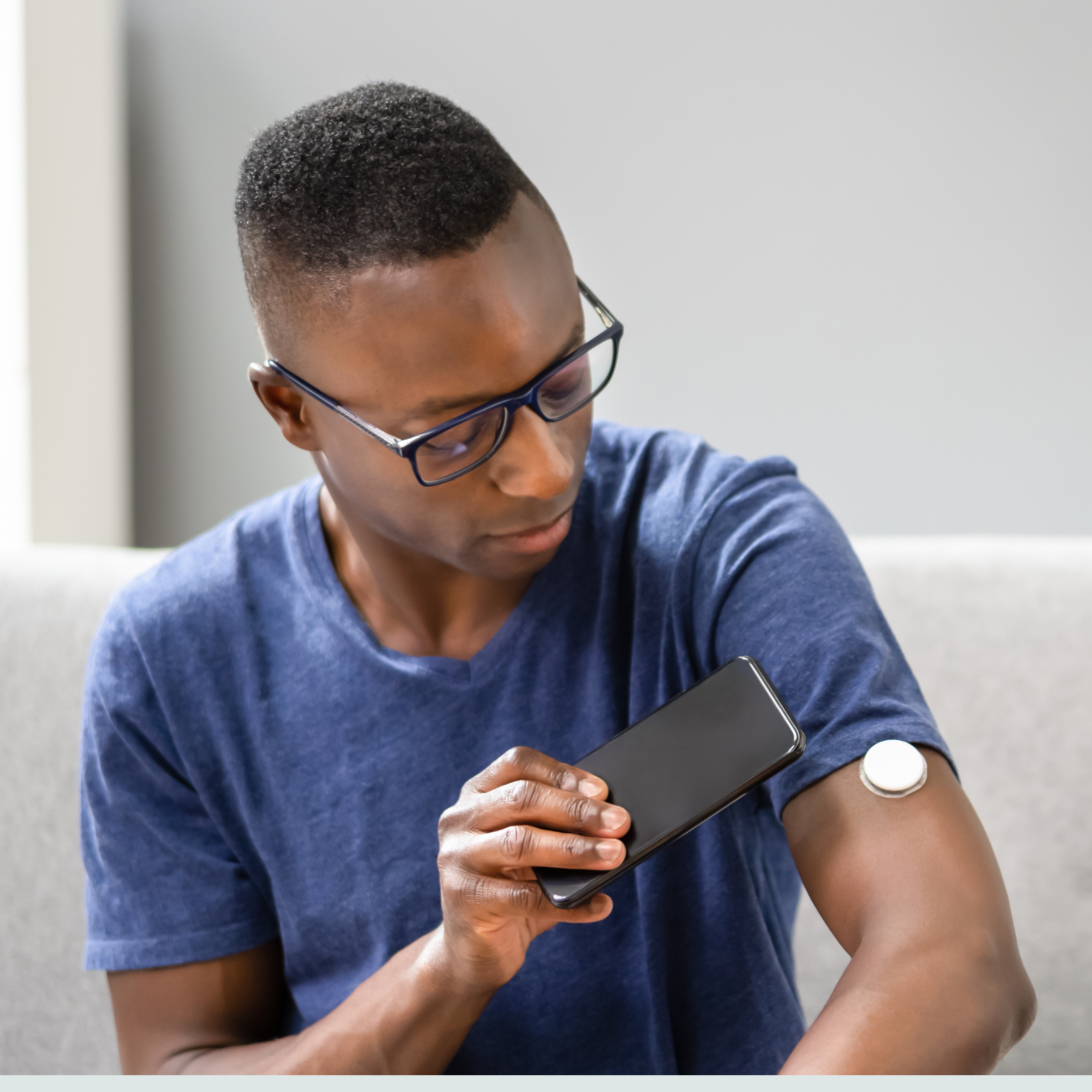
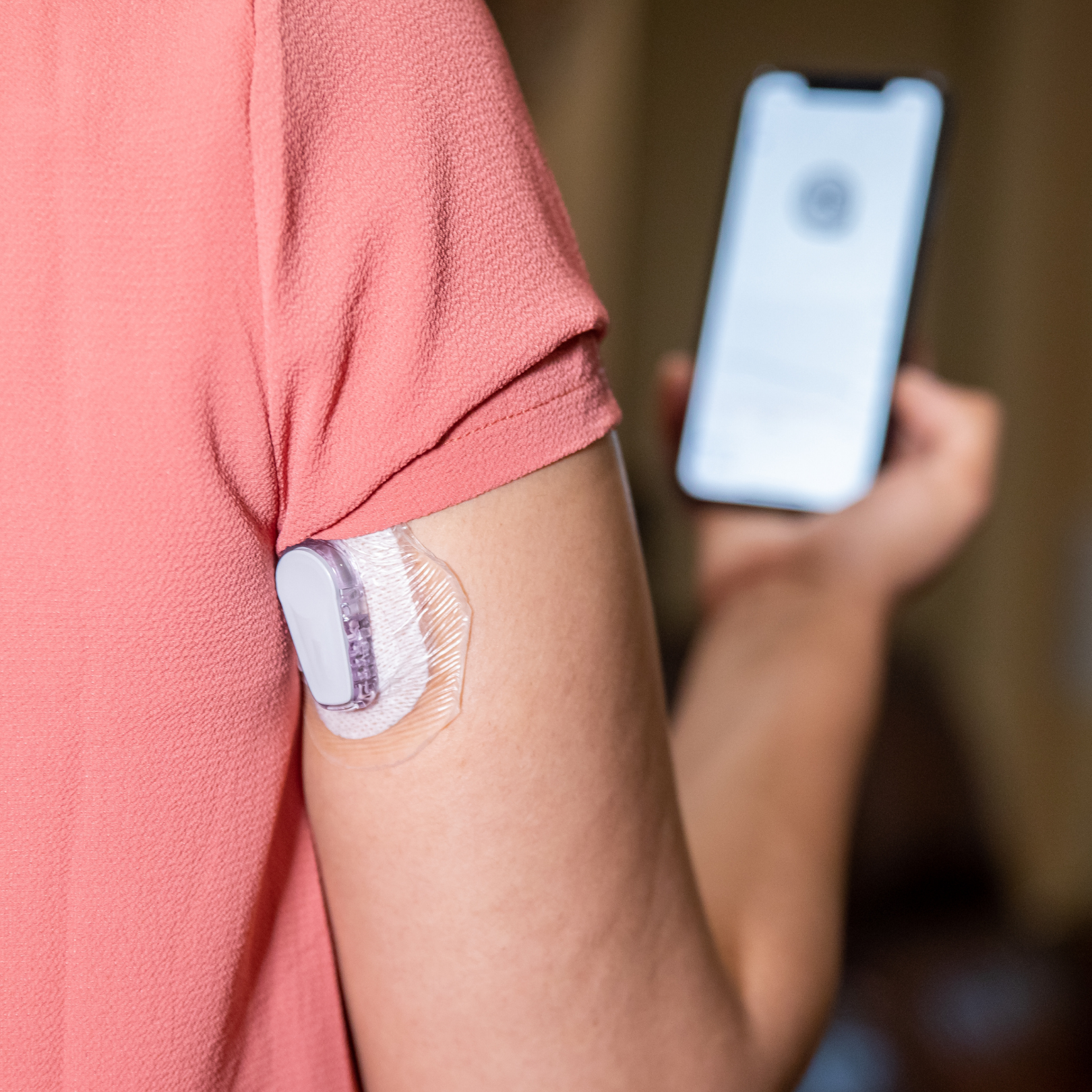
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) is a newer technology which allows very frequent monitoring/checking of blood sugar. To use a CGM, the user must insert a tiny filament into the subcutaneous space for up to a week at a time which is attached to a small transmitter which is adhesed to the skin. A signal is sent from the transmitter to a reading device. The CGM measures the sugar in the spaces between the fat cells. This reading correlates well with the actual blood sugar.
CGM gives the user the ability to monitor the blood sugar more comprehensively. The CGM monitors can be programmed to alarm if the patient is below or above a glucose threshold. We have used CGM extensively in Type 1 diabetes and it is sometimes used in Type 2 diabetes.
Insulin pumps are recommended for people with Type 1 Diabetes or Type 2 Diabetes on multiple doses of insulin per day. The insulin pump is used by people trying to improve their Diabetes control and is a must for people with frequent or problematic hypoglycemia. It offers flexibility in insulin dosing and offers more insulin dose adjustability than injection insulin. The pump is commonly used in pregnancy.
Thanks to research advances, there are more, and better, options available to treat Diabetes. Oral medications, which treat the deficiencies in Diabetes have been developed. The medications are effective and generally safer than older medications such as sulfonylureas. The newer medications tend to not cause hypoglycemia and they are associated with either weight loss or no weight gain. Oral medications are currently available, which increase insulin levels and lower glucagon. One oral medication induces the kidneys to lose glucose in the urine, thereby lowering the blood sugar.
One relatively new class of injectible meds is available to be given in daily and weekly injections. Insulin is also being developed which provides a more predictable background or basal insulin and faster mealtime insulins are being developed. Inhaled insulin has recently been approved as a rapid-acting mealtime insulin.
One of the most predictable ways to give insulin is with an insulin pump. Insulin pumps constantly infuse a small amount of insulin to provide a basal insulin. At mealtimes the user enters data, such as amount of carbohydrate to be eaten and the fingerstick sugar result to help calculate the mealtime insulin dose. In our practice, it is estimated that over 50-60% of people with Type 1 Diabetes are using insulin pumps.
Gestational Diabetes (GDM) is a frequent complication of Diabetes. Gestational Diabetes is the development of elevated blood sugar in pregnancy. Certain hormones produced by the placenta can lead to elevated blood sugar later in pregnancy. This problem can be diagnosed by doing a glucose tolerance test near the end of the second trimester. If untreated, GDM, can lead to excessive fetal weight gain and prematurity. GDM can be treated with dietary modifications and many times, insulin.
In 2015, it was estimated that 1 out of 3 adults has Pre-diabetes. Pre-diabetes can be diagnosed by checking a fasting blood sugar or by measuring the hemoglobin A1c (a 3-month average of blood sugar). People who are overweight or who have a family history of Diabetes are at high risk for Pre-diabetes (and for Diabetes). Most people with Pre-diabetes don’t know that they have this condition and it can only be diagnosed with a blood test. 50% of people with Pre-diabetes develop overt Diabetes in 10 years unless they are treated. The primary treatment of Pre-diabetes is exercise and weight loss. A 7% weight loss and the equivalent of 30 minutes of walking for 5 days of the week haven been shown to reduce progression of Pre-diabetes to Diabetes by nearly 60%. A medication, Metformin, is also frequently used to treat Pre-diabetes.
95% of people with Diabetes have Type 2 Diabetes. In 2015, it was estimated that 1 in 9 adults had this type of Diabetes. Type 2 Diabetes in usually diagnosed in the adult years though it can be seen in (usually overweight and sedentary) children. In Type 2 Diabetes, the cells that make insulin, beta cells, don’t produce sufficient amounts and there is also resistance to the effect of insulin on the body. Many people with Type 2 Diabetes can improve their blood sugar with weight loss and exercise alone. Others require treatments, which range from pills to injections of insulin and other injected medications. Successful treatment of Type 2 Diabetes has been shown to prevent or delay complications of Diabetes. People with Type 2 Diabetes are also at higher risk for heart diseases and treating their heart disease risk factors is important.
5% of people with Diabetes have Type 1 Diabetes. This type of Diabetes is usually diagnosed in childhood, yet many times it is diagnosed in adults, even in adults over the age of 50. People with Type 1 Diabetes take insulin for treatment since their beta cells (the cells that make insulin) no longer produce insulin due to auto-immune destruction. People with Type 1 Diabetes take insulin by injection or via an insulin pump. People with Type 1 Diabetes can lead a full, healthy life with proper management. Successful treatment of Type 1 Diabetes has been shown to prevent or delay complications tied to Diabetes.